ScrewCupNaviAR App
The App developed for augmented reality helping the surgeon during operation to navigate and position of the screw properly in cup. The App increase the accuracy, during trans acetabular screw placement

ScrewCupNaviAR App
Introduction
Indications for screws placement are acetabular deficiencies due to hip dysplasia related insufficient osseous coverage, osteopenic bone stock, post traumatic or radiated bone stock. Screws are effectively used as an alternative method cup fixation in total hip arthroplasty (THA) is augmented by screws. The benefits of use of screws are most secure fixation, prevents tilting of component and dislodgement, allows less press fit, better bone acetabular contact, less chance for acetabular fracture, prevent cup acutely come loose. Optimal screw hole positioning during placement of screw, strictly in periacetabular bone, avoiding injury to the near neuro-vascular structures is of paramount importance.
 |  |  |  |
|---|---|---|---|
 |  |  |  |
 |  |  |
Sturctures affected
Injury to a nerve or vessel associated with total hip arthroplasty (THA) can be a devastating complication that can lead to loss of function and, in some cases, loss of limb or life. Vascular injury in hip replacement surgery can be catastrophic follow by life threatening consequences, such as hypovolemic shock, pseudoaneurysm, thrombosis, and arteriovenous fistula formation, which may necessitate emergency vascular surgery, Bleeding from a major vessel should be high in the differential diagnosis if an acute sustained drop in blood pressure occurs during THA, particularly after screw placement. Vascular injury to the external iliac (femoral) and obturator vessels has been reported to range from 0.2% to 0.3% for screw placement.Vulnerable structures are the external iliac, obturator, superior and inferior gluteal, and internal pudendal arteries and veins and the obturator, superior and inferior gluteal internal pudendal, and sciatic nerves. Even when a patient has a mild nerve deficit that eventually recovers, it is stressful to both patient and surgeon during the recovery period. The trans acetabular fixation of screws necessitates drilling of the acetabular bone, followed by measurement of the depth of the bone and then, occasionally by tapping, and finally insertion of the screws that anchor the cup or cages into the osseous columns of the acetabulum. Frequent potential error is plunging especially during drilling. The screws should be placed in the areas of the acetabulum that provide the best bone stock for purchase while minimising the risk of damage to vital intra pelvic structures.
The quadrant system, in determining screw placement in hips with a normal center of
rotation, although helpful The quadrant system, in determining screw placement vision can be misleading in guiding screw Insertion
Acetabular-quadrant system
Acetabular-quadrant system is a well established system to help the surgeon with intra-operative orientation for safe placing the trans acetabular screw. The quadrants can be used to locate safe and dangerous zones. Surgeon during operation should palpate the Anterior Superior Iliac Spine (ASIS) and draw in his mind an imaginary line that divide the acetabulum to anterior and posterior halve. A perpendicular line divides each half into a superior and inferior quadrant. The posterior superior quadrant - a small area can accept screws longer than 35 mm- is considered the safest zone for screw placement because it consists of the greatest bone depth for secure screw fixation. although helpful The quadrant system, in determining screw placement , Surgeons vision and three dimensional perception of location of Neurovascular Structures , can be misleading in guiding screw Insertion it is subject to erroneously comprehension of intra pelvic structures, which are not visible, the most common mechanism of injury is intrapelvic screw placement by wrong trajectory of screw.
Acetabulum is divided into anterior and posterior halves by a line originating from the anterior superior iliac spine. Intra pelvic structures adjacent to the anterior quadrants include the external iliac vessels and the obturator vessels. Located opposite to the posterior inferior quadrant are the inferior gluteal and the internal pudendal vessels.
Structures at risk of penetration by screws include the external iliac vessels, the obturator nerve and vessels, the superior gluteal nerve and vessels, and the sciatic nerve. topographical map of periacetabular bone stock and neurovascular structures, the postero-superior and posteroinferior quadrants are usually relatively safe for screw fixation but not precise at he external iliac artery extended into the anterosuperior quadrant, and the obturator artery into the anteroinferior quadrant.
The app augments literally the surgeons vision by augmented and aiding his reality intraoperatively taking into account reference anatomical points and presenting live the actual quadrant system and safe zones by depicting in colours (green) or dangerous (red) by minimizing risk by avoiding injury to neural and vascular structures near to the osseous acetabulum, which the surgeon is not able to see during total hip arthroplasty to the surgeon during placement of the screws especially at multi hole cup.
Anatomical structures that are at risk during the transacetabular placement of screws, to detemine the relative contiguity of intrapelvic neural and vascular structures to screws placed in specific locations of Anatomical structures that are at risk during the transacetabular placement of screws, to detemine the relative contiguity of intrapelvic neural and vascular structures to screws placed in specific locations of the acetabulum, and to develop a quadrant system, with discernible operative landmarks, to guide in placement of the screws during primary and revision acetabular anhroplasty.
The acetabular-quadrant system provides the surgeon with a simple intraoperative guide to the trans acetabular placement of screws during primary and revision acetabular arthroplasty.The relationship between the intrapelvic neurovascular bundles and the osseous acetabular structures has been investigated and It should be recognized that the superior gluteal vessels are located beyond this quadrant. Knowing the location of the pertinent neural and vascular structures relative to the acetabular quadrant system can be helpful in avoiding neural and vascular complications during transacetabular screw placement based in surgeon experience. The anatomical structures that are contiguous to the acetabulum, are not visible to the surgeon during cup positioning in total hip arthroplasty and are subjectively estimated by surgeon 3D spatial perception who try to determine the optimal directions for placing screws. Behind the cup periacetabular anatomy is not in view during surgery The Trajectory of screw is surmised three-dimensionally and obscured during surgery
Description
Indications for screws placement are acetabular deficiencies due to hip dysplasia related insufficient osseous coverage, osteopenic bone stock, post traumatic or radiated bone stock. Screws are effectively used as an alternative method cup fixation in total hip arthroplasty (THA) is augmented by screws. The benefits of use of screws are most secure fixation, prevents tilting of component and dislodgement, allows less press fit, better bone acetabular contact, less chance for acetabular fracture, prevent cup acutely come loose. Optimal screw hole positioning during placement of screw, strictly in periacetabular bone, avoiding injury to the near neuro-vascular structures is of paramount importance.


The app allow the surgeon in Prosthetic Acetabular Reconstruction during trans Acetabular screw placement to
- real time quantitative understanding of the optimal depth screw purchase of sufficient bone stock at periacetabular osseous by simultaneuolsy avoiding dangerous areas
-define deeper and safer screw trajectories for transacetabular screw fixation in prosthetic acetabular reconstruction.
-depict in augmented Reality (AR) and project the Safe Zones defined by acetabular-quadrant system (Wasielewski RC et al ) vividly, helping during transacetabular screw fixation to navigate in real time and choose optimal location.
In case the tip of the screw is directed in dangerouly close to nerve or vessel field the value over approaching safe zone are green
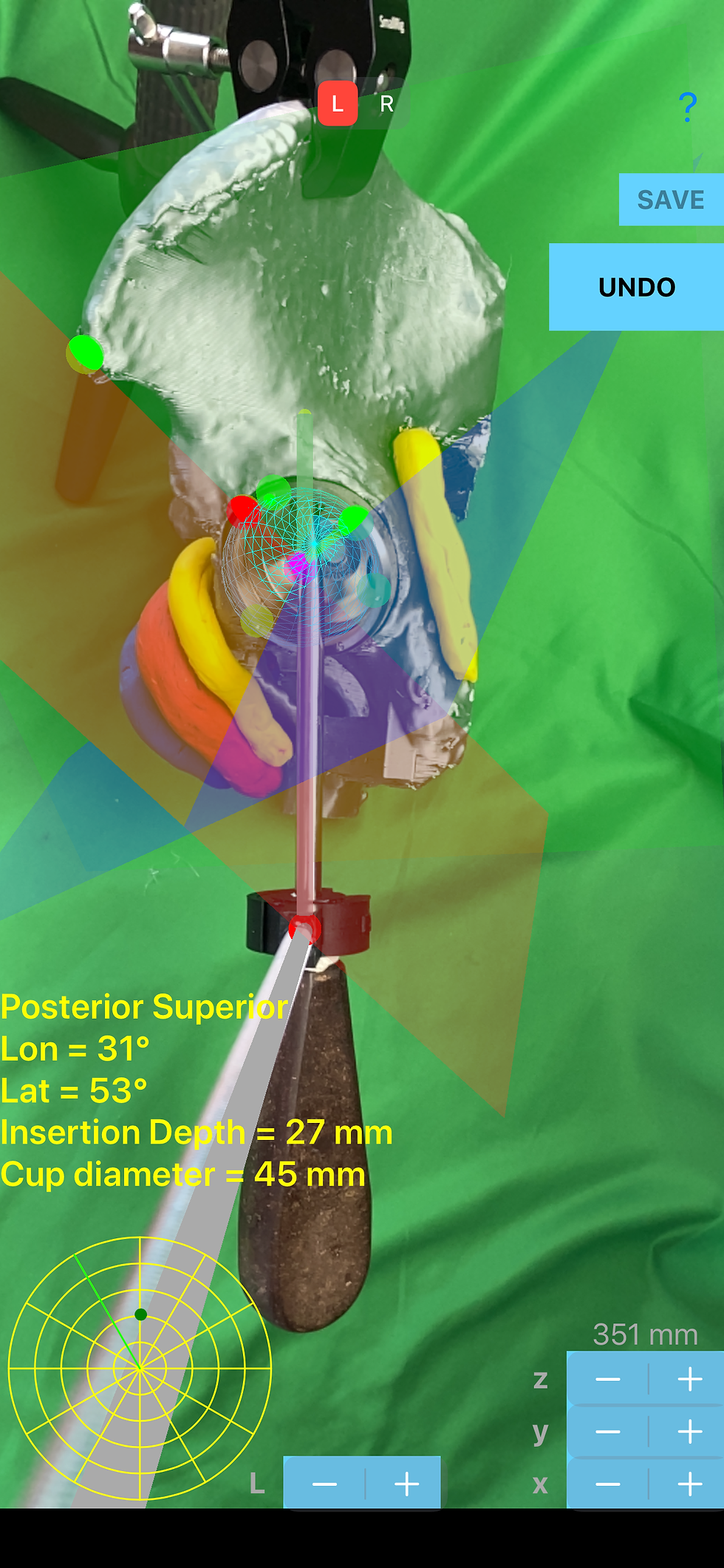
2-D topographical map according to the 3-D depth of the cup is depicted and act as a radar navigation map during screw placement -A 2D ‘dart board ‘ like drawing which is composed by same-centered circles (latidude) divided by lines (longitude) reflected the 3D depth cup hemisphere respectively - Radar screen -
The position of the tip of the screw is constantly reflected in real time in a radar screen by highlighting a dot in the respective semicircular topographical quadrant area of the ‘dart board like ‘ Radar screen.
The dot while inside a semicircular quadrants contained of Radar screen is changing colours in accordance to the spatial position of tip of the screw (deep green, green, light green, red ) reflecting the distribution of potentially sound screw bone purchase without harming the pelvic neuromuscular structures. The “greener” the dot in the semicircular quadrant in Radar screen the longer the screw that can be placed in this region of cup hemisphere.(Light green < 20 mm, green <35 mm , Deep green <40 mm)
-in real time corresponding longitude and latitude of the tip of screw are presented in scree. Knowing that the optimal locations for 2 screw-holes in the cup at 30°and 64° of latitude, with a separation angle of 35°between them starting at 17° longitude, now the surgeon can easily, accurately and objectively navigate avoiding injury to neurovascular structures.
-the distance in mm of the tip of screw to the shell of the cup , the insertion depth in mm of the screw is constantly presented on screen, negative values reflect that of the tip of screw is away from the shell of the cup and positive values that the tip of the screw has pass behind the cup shell and the tip of the screw namely inside the peri-acetabular bone and the actual depth of insertion in mm is given.
The color of the insertion depth is changing in green or red respectively according to the optimal safe depth in respective quadrant of the tip of the screw while the also the dot mark in radar screen follow the same pattern.
-the surgeon should attempt to position at least two the screw holes within safe zones
where bone stock and safety are optimized.
-Excessively long screws that protrude into neurovascular structure can be avoided
-The zones of optimal bone depth for screw purchase and simultaneously safe avoiding accidental injury
Therefore, optimizing cup placement involves achieving the best possible orientation while simultaneously positioning screw holes over the locations of maximal bone depth and safety.
Knowing the location of the pertinent neural and vascular structures relative to the ac-
etabular quadrant system at the high hip center can be very useful in avoiding neural and vascular complications during transacetabular screw placement.
Are the tip of the screw which is actually behind the cup in the pericatabural bone the Position of the screw is repressed in the dart board drawing over by highlighting the resceptive Quartrant of corespondenting the logitude and latitude
Help understand where screw is heading
By changing the bearing of the screw diver in real time the you can monitor where you you position is by observing the dot changing colour according to the allowed depth ( red represents from Same-centered circles
-Over the screen in real time in radar screen a dot corresponding to the direction of screw driver of insertion device depicted. Manipulating the Tool in real time the surgeon, the position of dot on and direction with accuracy in real time in augmented reality by observing the screen of the i-phone. Values in real time are printed in different colours in screen, red whenever the values fall outside the optimal depth ranges for .
-By monitoring live the depth and distance of the insertion the surgeon can’t be mislead by wrong perceptions, so can predict where to stop insertion of the trans acetabular screw controlling during handling without accidentally injuring neuromuscular structures.
-By monitoring live the depth of the cut the surgeon can’t be mislead by wrong perceptions, so can predict where to stop during handling with the reciprocating oscillating saw without accidentally injuring neuromuscular structures.
-The surgeon can be directed in real time by augmenting his vision reality by monitoring the readings of screen (radar) by observing not only the colour of the dot but also the position inside the subdivisions of the quadrants and perform intra operatively adjustments, simultaneously by manipulating the insertion tool by changing the direction or the insertion depth aiming at the safest part and of the peri acetabular bone quadrant
- insertion depth in mm and is presented in real time objectively.
-helps predict safe screw trajectories courses avoiding bearings that could jeopardise periacetabular neurovascular and musculotendinous structures thus longer screws placed in deeper pelvic bone stock allowing better fixation stability of cup
The possible safe zones are not guided only by the 4 quadrant system but newer smaller semicircular subdivisions areas inside the quadrants have been added according to the latest international literature
Accurate placement of screws in periacetabuler bony tissue is of paramount importance. Now the surgeon can obtain positional information by observing the dot over the radar on screen of the intended acetabular screw placement in direction and depth. The combination of Augmented reality environment and real surgery with planes and 3D topographical data in operative field intra operatively, aiding the ability of surgeon to perform precise screw acetabular insertion brings a new dimension in operational surgery.
All information received from the software output must be clinically reviewed regarding its plausibility before patient treatment! The App indicated for assisting during operation the Operator. Judgment and experience are required to properly use the App. The software is not for primary image interpretation. General knowledge of the location of the pertinent neural and vascular structures is given based on acetabular quadrant system , while not anatomical absolute, should be used with extreme caution by the surgeon during surgery .
Any influence the operators in making decisions during operation remains Surgeons own responsibility and experience. A surgeon must always rely on his or her own professional clinical judgement when deciding whether to use a particular technique when treating a particular patient. App does not dispense medical advice. It is recommended that surgeons must be trained in the use before using it in real surgery.
Reference
1. Liu Q, et all Safe zone for transacetabular screw fixation in prosthetic acetabular reconstruction of high developmental dysplasia of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009;91(12):2880-2885.
2. Wasielewski RC et all , . Acetsbularanatomy and the transacetabular fixation of screws in total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1990:72:501-8.
How can I use this App
For successful accurate screw cup placement during THA with the aid of ScrewCupNavi App, two physical devices: (a) the Case i-Phone - Probe tool (CIPT), and (b) the Clamp tool (CT) have to be 3D-printed, according to surgeon preference material (Stainless Steel, ULTEM or Peek which can be sterized according to manufacturer own specification and guidelines) - (STL or OBJ files can be sent to you after submitting your requested in the Contact Us form below
More details...
These devices have concrete dimensions, are calibrated for the app and are necessary for landmark registration and real time positional guidance.
The unsterilized i-Phone should be placed in a sterilized waterproof sealable bag. This is a common practice in surgical fields where non sterile parts are usually placed in sterile bags like arthroscopes, cameras, optical wires, tools etc. Sterile bags are readily available in operation rooms, taking always in to account bag manufacturer specification and guidelines. Plastic coverage should be transparent and not blur the iPhone cameras.
The surgeon should placed the iPhone in the case place of the Case i-Phone -Probe tool (CIPT) which is previously sterilised according to manufacture guidelines for the 3D printed material specification used.
In details:
A. Case i-Phone - Probe tool (CiPT). This device is dedicated for surface registration and the same instrument combined with the next instrument the clamp works as position detector. The tool consist of the case, in which the iPhone sits, and the rod. Rod has predefined length (32 cm) and it is attached perpendicular to the phones case, at the point where factory defined the centrum of the iPhone. This point is by default the origin in 3D dimensions namely 0,0,0 in XYZ axis. The other side of the rod is the side that acts as pointer tip location (z dimension).
In the Case i-Phone - Probe tool (CIPT) the case should be according to the dimensions of iPhone model used.
B. Clamp tool (CT). This tool is a simple clamp attached to shaft of screw driver or burr tool that has a slot designed to receive perpendicular the pointer tip side of the case i-Phone-probe tool (CiPT).The clamp can be securely fit to screw drivers shaft trough a hole so rotation of the tool handle is allowed while screw or burring and navigation is possible.
How it works. Method-technique
First the Case i-Phone - Probe tool (CiPT) - a device dedicated for surface registration - should be 3D printed, after downloading the appropriate 3D files according to user’s iPhone model from developer’s site. The device consist of the case, in which the iPhone sits and the rod. Rod has a predefined length ( 32cm) and it is attached perpendicular to the phone’s case. The other side of the rod is the side that acts as mechanical pointer tip location. The pointer tip sphere in augmented reality (AR) by the app should coincide with the mechanical pointer tip location of the rod in order to measure accurate.
Calibration is achieved by simply pressing the direction buttons (+,-) over the screen, the position (XYZ) of pointer tip sphere in augmented reality (red sphere) is adjusted accordingly. The user aim the pointer tip sphere in AR to be aligned in all dimensions and coincide over the mechanical pointer tip location of the rod of the i-phone in Case.
More specifically, by pressing the + or - button in the upper row, the (z) distance is adjusted respectively. It is recommended first to measure manually the distance from tip-pointer to case, by default this is 32 cm, and then calibrate the Z distance with the real distance from the case to tip of the pointer. The following x,y-calibration procedure is in two dimensions over the screen’s phone (x,y), aiming to bring the presented red sphere to coincide optically with actual pointer tip. By pressing the + or - button in the intermediate row for the (y) distance (up-down), and likewise the + or - button in the last row for the (x) distance (left-right), the distances are adjusted.
Operative set up The patient pelvis is in decubitus or lateral position for classic lateral approach of the hip for total hip replacement surgery by conventional usual fashion. Once the surgeon try to place the cup inside the bony acetabulum and decides to enhance the stability with screws he must follow the rest procedure before or ahas approach the actebulum.
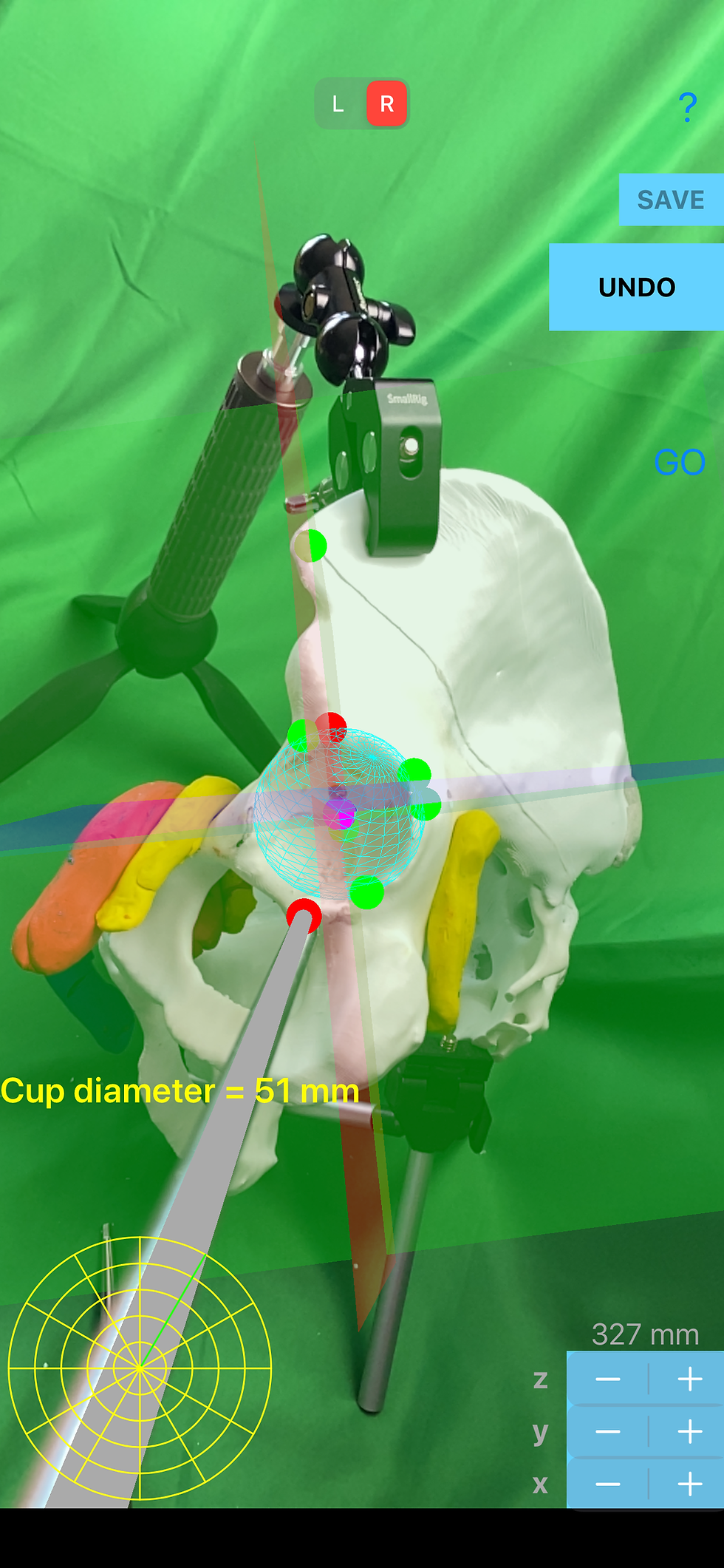
Cup Registration phase. The surgeon should select side, left or right by pressing the corresponding button. For selected side respective button remains red highlighted.
A green coloured marking sphere appears by touching any point over the screen in augmented reality during registration. By touching the tip pointer of the Case-Iphone-Probe Tool over the intended point and by touching the screen of iPhone simultaneously each time a green sphere appears in augmented reality.
Real time reading and measurements. By pressing the Go button Surgeon can view a grey cylinder projecting from red sphere at the clamp to yellow sphere superimposed in AR over the shaft of the real tool. The length of the presented in (AR) grey cylinder must end at the tip of the screw. The length of grey cylinder which ends at yellow sphere can be adjusted by pressing the + or - of L button over the screen in the same way, and must coincide with the tip of the real screw, in order to be calibrated and work properly. 2-D topographical map according to the 3-D depth of the cup is depicted and act as a radar navigation map during screw placement - A 2D ‘dart board ‘ like drawing which is composed by concentric circles ( latitude ) divided by lines ( longitude ), reflects the corresponding 3D depth cup hemisphere - Radar screen - A green line in Radar screen reflects the projected location of the Anterior Superior Iliac Spine (ASIS) where Longitude value is set to 0° and the increase in degrees towards 360° is counterclockwise or clockwise according to L or R measurement.
The yellow sphere now is reflected inside the radar screen as a coloured dot.
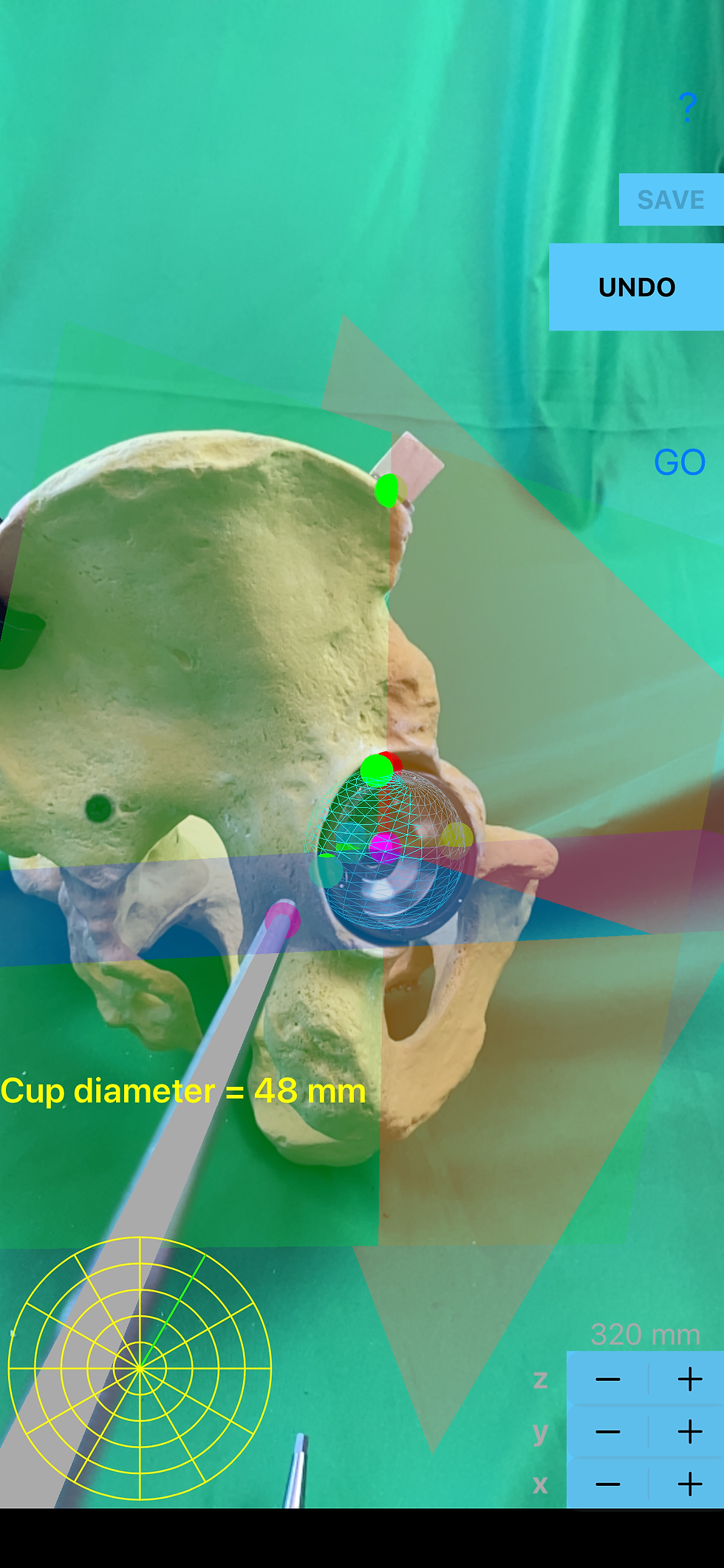
Once the surgeon has finally approached patients bony acetabulum and has place the cup, registration is performed with the pointer tip of the CIPT. Four points required: Three points at marginal circumference of bony acetabulum rim or cup - one in anterior superior lip (A1), one in posterior superior lip (A2) and one in posterior inferior lip (A3) - The forth point in order to complete the cup registration should be at the deepest part of the cup (A4). By the registration of the last point (A4) a blue transparent sphere also appears in augmented reality touching the cup or acetabular floor, all acetabular surface, and circumference of the real acetabulum or cup. Inside the blue sphere a magenta sphere appear depicting the center of rotation.
Acetabular-quadrant System is a well established system for safe placing the trans acetabular screw. (Wasielewski RC et all , Acetabularanatomy and the transacetabular fixation of screws in total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1990:72:501-8). Quadrant zones are formed by line drawn from ASIS to center of acetabulum second line drawn perpendicular to first line four quadrant are formed. (posterior-superior, posterior-inferior, anterior-inferior, anterior-superior quadrant)
By touching the tip pointer of the Case-Iphone-Probe Tool over the Anterior Superior Iliac Spine (ASIS) (S5) and by touching the screen of iPhone simultaneously, a red sphere appears over the Anterior Superior Iliac Spine (ASIS) (S5) in augmented reality, and also three perpendicular planes appear passing the center of the cup towards the S5 with different hazy transparent colours (sagittal-blue, coronal-red, transverse-green) in augmented reality (AR), depicting the quadrant system in 3D space over the cup. The dimension of cup diameter is presented in mm.
Manipulating the handle of screw driver the dot colour and location in “radar” screen change respectively, in real time.
Over the screen also in real time the following dynamic values are presented, respectively:
a. The Current location of the tip of the screw, in relation to Quadrant zone in acetabular-quadrant System namely posterior-superior or posterior-inferior or anterior-inferior or anterior-superior quadrant.
b. The Longitude of the tip of the screw, taking values between 0° and 360°, values increase counterclockwise direction from green line.
c. The Latitude of the tip of the screw taking values between 0° and +90° degrees - by default the deepest part of cup is the pole and takes value of 90°.
d. The Insertion Depth is measured in mm namely the distance from the shell back surface of the cup to the tip of the screw. When the tip of the screw is proximal to the cup values are negative, when it is over the shell of the cup the insertion depth is 0, and when the tip of the screw is behind the back shell, inside the osseous acetabulum values are positive. The colour of the measured values is turning red incase the tip of the screw is in danger zone in real time.
Dot reflects in Radar screen in real time the current position of screw tip location and direction in 3D projection inside smaller semicircular subdivisions areas of the quadrants of the cup. Colour of the dot is changing continuously according to the depth of maximum bone purchase allowed in mm, while the tip of the screw is inserted in corresponding semicircular subdivisions areas of the quadrants of the reflected topographical map, with already known values from the International Literature optimum depth screw limit. Levels of green correspond to certain permitted depth accordingly. Light green colour of the dot in the radar screen reflects that the maximum safe depth for screw placement is less than 20 mm, in other words if real screw passes this value while the tip of the screw is in this area, the colour of the dot in the radar screen will not remain light green but turns red. Likewise for others areas, Green colour is for less than 35 mm, and Deep green colour is for more than 35 mm.
The powerful undo feature gives the user the freedom to make corrections without resetting the whole procedure. Simply by clicking the undo button the measurement returns to previous chosen point and thus registering once again the same anatomical landmark, without reseting the whole procedure and avoid starting over again.
In quick review:
Cup registration.
Following points should be collected at circumference of the cup rim:
A1 - anterior superior lip
A2 - posterior superior lip
A3 - posterior inferior lip
A4 - deepest part of the acetabulum
S5 - Anterior Superior Iliac Spine (ASIS)
Screen readings:
Cup diameter of the acetabulum in mm
Current Quadrant zone - current position of tip of the screw in Acetabular-quadrant System ( values are posterior-superior, posterior-inferior, anterior-inferior, anterior-superior quadrant)
Lon = Longitudes: values between 0° and 360°
Lat = Latitudes: values between 0° and +90° degrees deepest part of cup pole 90°
Cup diameter in mm
Insertion Depth ID in mm - values 0 over the shell, positive value reflects that the tip is behind cup inside bony acetabulum, otherwise negative.
Radar screen - 2D topographical map according to the 3D topographical map reflection of the cup, divided by smaller semicircular subdivisions areas inside the quadrants.
Green line - position of the Anterior Superior Iliac Spine (ASIS) where Longitude value is 0°
Dot - reflects in Radar screen in real time the current position of screw tip location and direction in 3D in smaller semicircular subdivisions areas inside the quadrants .
Colour of the dot - change according to the depth of maximum bone purchase allowed in mm. levels of green, Light green < 20 mm, Green <35 mm, Deep green 35>mm
Red danger
Buttons adjustments
Button highlighted left or right Side accordingly
Undo button
z + or - buttons in the upper row —> adjust the (z) distance-depth
y + or - buttons -in the intermediate row —> adjust the (y) distance, up-down
x + or - button s -in the last row the + - button —> adjust the (x) distance, left-right
L + or - button enlarge or reduce length of grey cylinder ending to yellow sphere in order to be calibrated in AR with the actual screw driver shaft length, namely the tip of the real screw should coincide with the yellow sphere.
All information received from the software output must be clinically reviewed regarding its plausibility before patient treatment! The App indicated for assisting during operation the Operator. Judgment and experience are required to properly use the App. The software is not for primary image interpretation. Any influence the operators in making decisions during operation remains Surgeons own responsibility and experience. A surgeon must always rely on his or her own professional clinical judgement when deciding whether to use a particular technique when treating a particular patient. App does not dispense medical advice. It is recommended that surgeons must be trained in the use before using it in real surgery.
Tutorial ScrewCupNaviAR App aid for simultenouelsy 2 or 3 screw holes selection of insertion
The cup hemisphere is given the following values
Long=Longitudes: values between 0° and 360°
Lat=Latitudes: values between 0° and +90° degrees deepest part of cup pole 90°
0° degree of latitude is defined at the rim of the cup and 90° of latitude at the pole of the hemispheric cup. The direction pointing at the anterior superior iliac spine is defined as 0° longitude, and the longitude value increased counterclockwise to 360 °.
To ensure safety and facilitate at least 2 deep screw purchase of bone stock simultaneously, numerical data presented on screen readings (longitude and latitude) of the app might help surgeon to find the corresponding optimal longitude for 30° and latitude to 17° for the first screw placement and aiming for the second screw at 64°, the latitude and 52° longitude value which according to international literature are the best for cluster placement of screws trans acetabular screw placement this could be also help full to place the commercial cups into the acetabulum with given screw-hole locations
The app may provide a reference for screw-hole placement of acetabular cups and adjusting the 3D rotation of the cup ,while inside the bony acetabulum, during insertion and accommodate thus respectively at least 2 screws to gain purchase into the deepest bone stock and yet not jeopardise the vascular structures.
The app provides intraoperatively, succint topographical map of periacetabular depth bone stock and safe zones in relation to neuro vascular structure based on anatomic studies reported by Wasielewski et al ,the optimal locations for 2 screw-holes are at 30°and 64° of latitude, with a separation angle of 35°between them
The cup is a hemisphere and 0° degree of latitude is defined at the rim of the cup and 90° of latitude at the pole of the hemispheric cup. The direction pointing at the anterior superior iliac spine is defined as 0° longitude, and the longitude value increased counterclockwise to 360 °.
Acetabular components that provide through holes varying amounts of freedom to angle the screw from perpendicular allow to insert from otherwise dangerous positions, screws can be directed posteriorly especially when the position of the second required screw-hole is not optimal, and rotating of the cup to allow purchase into deeper bone stock is impossible.
